T4
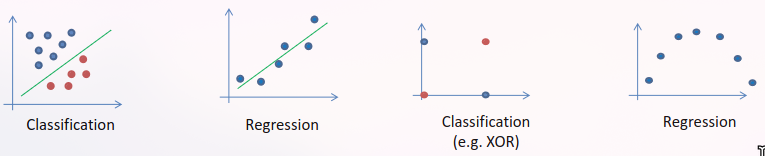
Linear Models
- Characterized by the simplicity of calculation snd analysis
- Linearity is defined in terms of functions with the properties:
- Used for classification (separation between classes) or regression
- Does not solve non-linear problems
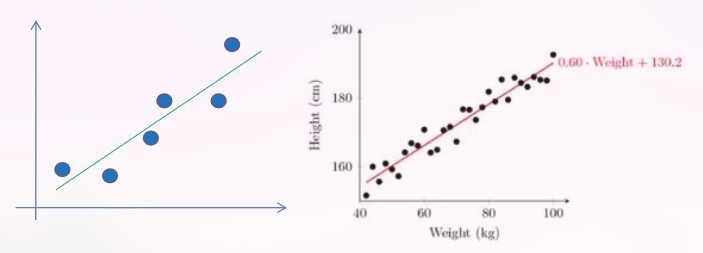
Linear Regresion
Aims to predict the value of a outcome, Y, based on the value of a predictor variable, X.
- Fit a straight line into a data set of observations;
- Use this line to predict unobserved values.
Models
Represent the relationship between input variables 𝒙𝟏, ..., 𝒙𝒏 (independent variables), and an output variable y (dependent variable).
Model (h) prediction given by (for the i-th example):

Multiple linear regression
- Multiple regression is used to determine the effect of a number of independent variables, x_1, x_2, x_3, etc on a single dependent variable, y
- The different x variables are combined in a linear way and each has its own regression coefficient (θ):

The θ parameters reflect the independent contribution of each independent variable, x, to the value of the dependent variable, y.
Visualization
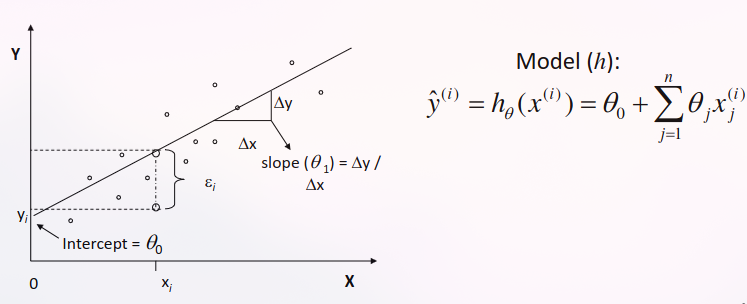
Usually using “Error/loss (cost) function” and minimizing its value (minimize the squared-error between each point and the line)
mean squares errores (MSE)
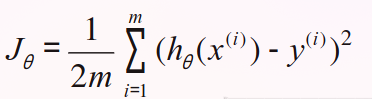
J is a function of the model parameters θ_1, ..., θ_n
𝐡_𝛉(𝐱^(𝐢)) is the value predicted by the model, ŷ ^(𝐢)
𝐲^(𝐢) is the real value
Objective: to identify the parameters of the model in order to minimize the value of J
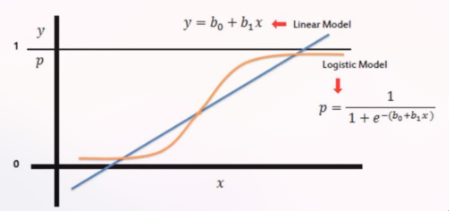
Logistic Regression
- Discrete dependent variable: classification problem
- Uses regression models for binary classification by interpreting the model output in order to extract a class