T - Aula 3
2 de Outubro, 2023 - #ASCN
1. Provisioning
Provisioning is the action of providing or supplying something for use.
- Server provisioning
- Storage provisioning
- Network provisioning
- VM provisioning
- User provisioning
2. Deployment
Deployment is the process of installing or upgrading an application/service into a server.
- Installing or upgrading a web application (files, migrations, assets...)
- Network service installation or upgrade
- The scope is the service or application
Provisioning and deployment are boring after the 1st iteration...
- repetitive process
- may spread across multiple and heterogeneous systems
- will probably require tweaks overtime
- sometimes a time consuming task
3. Configuration Management
A way of handling systematic system changes while maintaining integrity throughout its lifecycle.
- Express configuration through a common dialect
- Predictable configuration result
- Configuration evolves with the infrastructure
- Infrastructure documentation as a positive side effect
- Full history of changes overtime when used with source code management
- Changes are observable
- Process Automation
- Each unit of work is expressed as a recipe
4. Recipes / Reuse / Automation
Define task automation via a set of directives expressed in a language.
#!/bin/sh
username = deployer
apt-get -y update
apt-get -y upgrade
apt-get -y install vim-nox openntpd sudo whois aptitude
useradd -G sudo -p "password" -s /bin/bash -m $username
mkdir -p /home/$username/.ssh
chmod 700 /home/$username/.ssh
chown $username: /home/$username/.ssh
echo "public_key" >> /home/$username/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 600 /home/$username/.ssh/authorized_keys
chown $username: /home/$username/.ssh/authorized_keys
5. Tools of the Trade
| Language | Agent | Agentless | SSH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ansible | YAML | No | Yes | Yes |
| Chef | Ruby | Yes | Supported | Yes |
| Puppet | Puppet's Dec. Lang. | Yes | Supported | Yes |
| SaltStack | YAML | Yes | Supported | Yes |
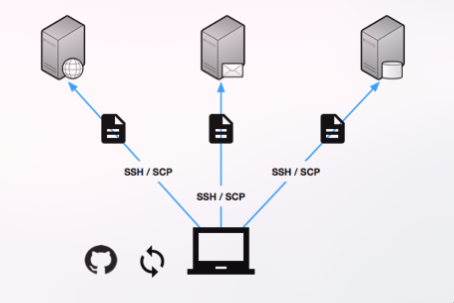
6. Provisioning and Deployment Workflow
7. Vocabulary
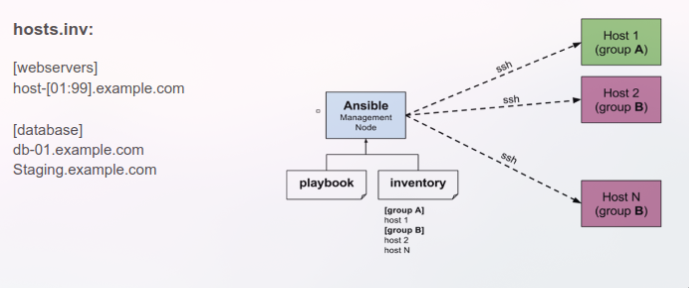
- Inventory - Grouped deployment targets (hosts)
- Module - Reusable work unit distributed with Ansible or developed for it
- Task - Combination of a module and given arguments in order to create an action
- Handlers - Special kind of task that responds to a notification
- Templates - Enable the creation of dynamic configuration (leverages Jinja2, the Python template engine)
- Role - Reusable component that encapsualtes variables, templates, tasks, handlers... (configurable)
- Playbook - Describe policies for remote systems to enforce (set of roles/tasks)
8. Overview
- Agentless recipe execution via SSH or locally
- Recipes are expressed in YAML
- Recipes are created via module and task directives
- Recipes are organzied into roles and playbooks
- Target hosts are defined in the inventory
- Tasks only run if the target differs from the expected result (idempotency)
9. Inventory
10. Playbook
- hosts: all
vars:
username: someuser
shell: /bin/bash
tasks:
- name: create unpriviledged user
user:
name: '{{username}}'
password: 'secretpasswordhash'
shell: '{{shell}}'
- name: Set SSH authorized_key
authorized_key:
user: '{{username}}'
state: present
key: "{{lookup('file', '/home' + someuser + '/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}"
11. Playbook with Roles
hosts.inv
provision.yml
roles
|
|- role
|- files (static files)
|- templates (Jinja2 templates)
|- tasks (task definition - main.yml)
|- handlers (handlers that trigger on notify - main.yml)
|- vars (role scoped variables - main.yml)
| ... (defaults, meta, etc)
Example:
- hosts: webservers
roles:
- config
- users
- ssh-server
- ntp-client
- ...
12. Execution
Without ansible.cfg:
ansible-playbook plabook.yml -b -i hosts.inv -u someuser -K --private-key=/path/to/private_key
With ansible.cfg (ansible.cfg):
ansible-playbook playbook.yml -b -K
ansible.config
[defaults]
hostfile = hosts.inv
remote_user = someusername
private_key_file = /.../someuser_private_key
Flags
-b -> become, priviledge elevation with sudo command
-i -> inventory file to sue
-u -> login username
-K -> ask sudo password
13. Leveling up...
13.1 Handlers
- name: template configuration file
template:
src: template.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify:
- restart nginx
handlers:
- name: restart nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
13.2 Conditionals
- name: Common Debian
include_tasks: debian.yml
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
- name: Common RedHat
include_tasks: rh.yml
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
when:
- condition
- condition
when: condition or condition
when: somevar | failed
when: somevar is defined
13.3 Loops
- name: Install Packages
apt: name="{{item}}" update_cache=yes state=latest
loop:
- vim-nox
- aptitute
- name: Install Packages
apt: name="{{item}}" update_cache=yes state=latest
loop: "{{list_variable_with_packages}}"
- name: Copy Files
copy: src="{{item.source}}" dest="{{item.destination}}"
loop:
- {source: 'motd', destination: '/etc/motd'}
- {source: 'sshd', destination: '/etc/ssh/sshd_config'}
13.4 Host Facts
Facts can be accessed and used within tasks and templates allowing for more dynamic playbooks.
{% for host in groups['webservers'] %}
{{ hostvars[host]['ansible_all_ipv4_addresses'] | join }}
{% endfor %}
{{ ansible_distribution }}
{{ ansible_os_family }}
{{ ansible_processor_vcpus }}
13.5 Vault
- Allows keeping sensitive data such as passwords or keys in encrypted files, rather than as plaintext in playbooks or roles
13.6 Provisioning GCP with Ansible
- Ansible can be used to provision different GCP sevices
- VMs, Kubernets, ...
- Ansible Modules (examples...)
- gcp_compute_disk
- gcp_compute_network
- gcp_compute_address
- gcp_compute_firewall
- gcp_compute_instance
- gcp_container_cluster
13.7 Dynamic Inventory
- When provision happens dynamically the addresses are unknown
- Problem has two solutions
- Manually (go into console and look at the addresses)
- Automatic (use a dynamic inventory)